Control Valve
manipulates a flowing fluid, such as gas, steam, water, or chemical compounds, to compensate for the load disturbance and keep the regulated process variable as close as possible to the desired set point
To See More Details Download Catalog Below:

About GAZAR Control Valve
Performance and safety are two of the key concerns in plants today. Since control valves are the only devices in the control loop that actually move to adjust the process, their performance is fundamental. If they don’t perform properly, you can’t meet production schedules and maintain product quality. GAZAR control valve (Globe, Rotary) manipulates a flowing fluid, such as gas, steam, water, or chemical compounds, to compensate for the load disturbance and keep the regulated process variable as close as possible to the desired set point. The control valve assembly typically consists of the valve body, the internal trim parts, an actuator to provide the motive power to operate the valve, and a variety of additional valve accessories, which can include positioners, transducers, supply pressure regulators, manual operators, or limit switches.
GAZAR Globe Control Valve
Our control valves are available in a variety of sizes (NPS ½ thru 24) and provide users with performance and flexibility. They can help solve an array of application needs from big to small, hot to cold, general to severe. GAZAR globe control valves have a selection of valve cages or plugs that can be interchanged to modify the inherent flow characteristic to linear, equal percentage, or quick opening to meet capacity demands.
GAZAR Rotary Control Valves
Rotary control valves generally have much higher maximum capacity than globe valves for a given body size. This fact makes rotary control valves attractive in applications where the pressure drop is rather small. Rotary control valves include ball, high-performance butterfly (used in throttling applications requiring large flow capacities (from NPS 2 to 72)).

Actuator for Control Valve
Pneumatically-operated control valve actuators are the most popular type in use, but electric, hydraulic, and manual actuators are also widely used. The spring-and-diaphragm pneumatic actuator is most commonly specified due to its dependability and simplicity of design. Pneumatically-operated piston actuators provide high stem force output for demanding service conditions. Adaptations of both spring-and-diaphragm and pneumatic piston actuators are available for direct installation on rotary control valves.
Diaphragm Actuators
Pneumatically-operated diaphragm actuators use air supply from controllers, positioners, or other sources, including various style such as:
1. Direct-acting, in which the increasing air pressure pushes the diaphragm down and extends the actuator stem.
2. Reverse-acting, in which the increasing air pressure pushes the diaphragm up and retracts the actuator stem.
3. Reversible, in which actuators can be assembled for either direct or reverse action.
4. Direct-acting unit for rotary valves, in which the increasing air pressure pushes down on the diaphragm, which, depending on orientation of the actuator lever on the valve shaft, may either open or close the valve.
Piston Actuators
Piston actuators are pneumatically operated using high-pressure plant air up to 150 psig (10.3 bar), often eliminating the need for a supply pressure regulator. Various accessories can be incorporated to position a double acting piston in the event of supply pressure failure, including pneumatic trip valves and lock-up systems.

Manual Actuators
Manual actuators are useful where automatic control is not required, but where ease of operation and good manual control is still necessary.
They are often used to actuate the bypass valve in a three-valve bypass loop around control valves for manual control of the process during maintenance or shut down of the automatic system.
Electric Actuators
Electric actuator designs use an electric motor and some form of gear reduction to move the valve plug. While electric actuators have traditionally been limited to on/off operation, some are now capable of continuous control. The use of brushless motors in electric actuators can reduce or eliminate motor burnout associated with turning the motor on and off rapidly. The initial purchase price still tends to remain above that of pneumatic actuation.
Integrated Accessory Attachment
• Eliminates external tubing reduced height and weight
• Entire actuator top works can be rotated 360° without disassembly
Self-adjusting PTFE V-ring Packing
• Maintenance-free design
• Low friction
• Roller burnished stem reduces friction external leakage, and maximizes packing life beyond what basic polishing can offer from competitors.
• Double wall design
• Small valve travel results in a long bellows life
• Modular design allows for the addition or removal of assembly bellows in the field
• Straight Thread Seat Design No cage, gaskets or seals required trim Fewer spare parts required for maintenance Easy removal even after many years of service.
• Various Noise Attenuation Options Flow Divider I, II, & III (Gases/Vapors) Anti-Cavitation Trims (Liquids) Optional downstream orifice plates
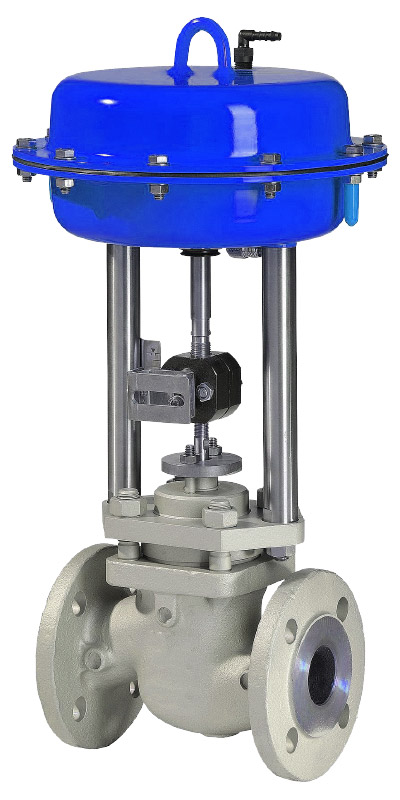

Rolling Diaphragm
Greatly reduces diaphragm wear compared to Stretching diaphragm design used by competitors Diaphragm design results in very small external air loss
Single Bonnet/Yoke Design
Actuator removal without the need to open the valve Bonnet and body of the valve always have same metallurgy Fewer components results in a lower profile valve
Low Lying Guide Bushing
Ensures precise plug alignment for our stem guided
Multiple Plug Designs
• Parabolic: Cost effective & debris friendly
• V-Port: Reduced vibration & debris friendly
• Perforated: Vibration reduction and flow dispersion
GAZAR Internal Strength
Trim For Every Application Obstacles hindering accurate process control can be numerous. GAZAR Control Valves comes equipped with a wide range of available trim options to overcome difficult to control applications.
1. Parabolic Plug 2. V V-Port Guided Plug 3. V Perforated Plug 4. V Multi-Stage Trim 5. Noise Attenuation Trim
Noise Reduction
When not getting noticed is a good thing
A flow divider is an optional internal device used with gases and vapors to help reduce the sound pressure level (SPL) of a valve. By creating an additional stage of pressure reduction inside the valve, it breaks a single large flow stream into multiple smaller flow streams, resulting in reduced noise emissions.
1. Steam Service 2. PSA (Pressure-Swing Adsorption) 3. Toxic and Corrosive Processes 4. Cryogenics
Technical Details
Valve Size: NPS 1/2 to 24 | Pressure Rating: ANSI Class 150 to 1500 | End Connection: Flanged: All ANSI Versions, Welding Ends: According to ANSI B16.25, Threated Ends: Up to NPS 2, ANSI 250 class only | Materials: Carbon Steel (A216 WCC, A352 LCC, & A217WC6) | Temperature Range: -325 to 842°F (-196 to 450°C) | Internal Leakage Rate: Class IV,V, or VI according to ANSI/FCI 70-2 and IEC 60534-4 | Extensions: Standard/Insulating/Bellows Seal | Packing: Spring-Loaded Low Emission V-ring Packing
GAZAR Control Valve Sizing
Control valves handle all kinds of fluids at temperatures from the cryogenic range to well over 538°C (1000°F). Selection of a control valve body assembly requires particular consideration to provide the best available combination of valve body style, material, and trim construction design for the intended service.
Capacity requirements and system operating pressure ranges also must be considered in selecting a control valve to ensure satisfactory operation without undue initial expense. Following information be provided for any set of conditions deemed important:
• Type of fluid to be controlled
• Temperature of fluid
• Viscosity of fluid
• Concentrations of all constituents including trace impurities
• Process conditions during startup, normal operations, and shutdowns
• Chemical cleaning that may occur periodically
• Specific gravity or density of fluid
• Fluid flow rate I
• Inlet pressure at valve
• Outlet pressure or pressure drop
• Maximum permissible noise level, if pertinent, and the measurement reference point
• Degrees of superheat or existence of flashing, if known
• Inlet and outlet pipeline size and schedule
• Special tagging information required
• Cast body material (ASTM A216 grade WCC, ASTM A217 grade WC9, ASTM A351 CF8M, etc.)
• End connections and valve rating (screwed, Class 600 RF flanged, Class 1500 RTJ flanges, etc.)
• Action desired on air failure (valve to open, close, or retain last controlled position)
• Instrument air supply available
• Instrument signal (3 to 15 psig, 4 to 20 mA, HART, etc.)
Control Valve, Design BF

Specifications: Globe-Style, Economical | Stem Guide Equal | Percentage – Flow Up | Bullet Form in Steel or Stainless Steel Bodies | Equal to Maximum Inlet pressure 1500 Psig From (-20 to 450°F) | Screwed or Socket weld End Connections
Description | Standard | NACE-MR0175 | NACE-MR0175 |
|---|---|---|---|
Body | WCB | WCB | 316 SS |
Bonnet | WCB | WCB | 316 SS |
Stem | 316 SS | 316 SS | 316 SS |
Seat Ring | 316 SS | 316 SS | 316 SS |
Valve Plug | 316 SS | 316 SS | 316 SS |
Guide Bushing | 17-4 PH SS | 17-4 PH SS | Hastelloy C |
Control Valve, Design BT
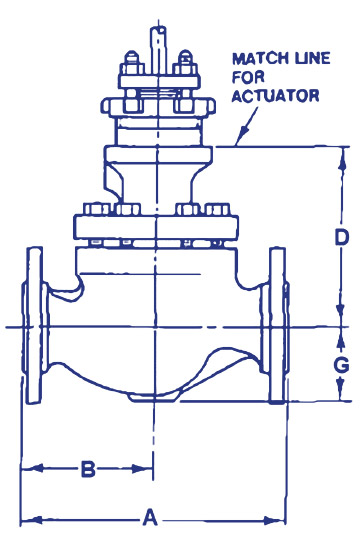
Specifications: Bodies are Globe-Style Valves | Full Capacity Trim: Quick Opening, Linear or Equal Percentage | Bullet Type, stem guide
Description | Standard | NACE-MR0175 | NACE-MR0175 |
|---|---|---|---|
Body | Cast Iron | WCB Steel | 31 6 SST (CF8M) |
Cage | 17-4 PH SST | 316 SS | 316 SS |
Seat Ring | 410 or 416 SS
(Hardened) | 316 SS / Alloy 6 Seat | 316 SS |
Valve Plug | 416 SS
(Hardened) | 316 SS / Alloy 6 Seat | 316 SS |
Guide Bushing | 17-4 PH SST | Alloy 6 | Alloy 6 |
C-Type Ball Valve

Specifications: Modified equal percentage | PTFE Packing: -46 to 232 C | Graphite Ribbon Packing: -198 to 427 C | -46 to 260 C, 150 & 300 LB
Description | Standard | NACE-MR0175 | Stainless steel |
|---|---|---|---|
Body | ASTM A216 Gr. WCC | ASTM A216 Gr. WCC | ASTM A351 Gr.CF8M |
V-notch Ball | ASTM A351
Gr.CF8M | ASTM A351 Gr.CF8M | ASTM A351 Gr.CF8M |
Shaft | S20910/Monel | S20910 | 17-4PH |
Bearing | Peek/PTFE | PEEK/PTFE | PEEK/PTFE |
Valve Shaft | PTFE | PTFE | PTFE |
Eccentric Ball Valves
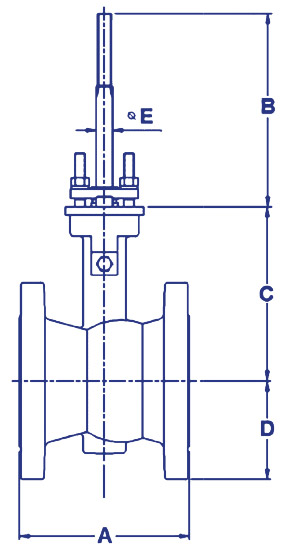
Specifications: Modified linear | PTFE V-ring: –198 to 232 C | Graphite: –198 to 425 C,150 & 300 LB
Description | Standard | NACE-MR0175 | Stainless steel |
|---|---|---|---|
Body | ASTM A216 Gr. WCC | ASTM A216 Gr. WCC | ASTM A351 Gr.CF8M |
Valve Plug | Chrome-Plated
316 SS | Alloy 6 | 316 SS |
Shaft | 316 SS | 316 SS | 316 SS |
Guide Bushing | 440 SS/Alloy 6 | 316 SS | PEEK/PTFE/Alloy 6 |
Valve Shaft | S20910
(Nitronic 50) | S20910
(Nitronic 50) | S20910
(Nitronic 50) |
Control Valve, Design HP

Specifications: High-Pressure, Globe Valve | Metal Seats, Cage Guide | 2160 psi (149 bar) For Two | Stage Cage and 3000 psi (207 bar) | For Three-Stage Cage | Equal percentage,Modified Equal Percentage, Linear
Description | Standard | NACE-MR0175 | Stainless steel |
|---|---|---|---|
Body | WCB steel | WCB steel | 316 Stainless Steel |
Valve Plug | 442 Stainless Steel | 17-4PH stainless steel with Alloy 6 | 316 Stainless Steel with Alloy 6 |
Cage | 17-4PH Stainless steel | 17-4PH Stainless steel | 316 Stainless Steel Electrolyzed |
Seat Ring | 416 Stainless Steel | Alloy 6 | Alloy 6 |
Seat Ring Retainer | 416 Stainless
Steel | Inconel 718 Heat Treated Electrolyzed | Inconel 718 Heat Treated Electrolyzed |
Control Valve, Design PT

Specifications: Globe Style | Cage Guide | Quick- Opening, Linear, Equal Percentage | Anti-Noise: Always Up | Anti-Cavitation: Always Down | High-temperature | High-Pressure is available too
Description | Standard | NACE-MR0175 | Stainless steel |
|---|---|---|---|
Body | WCB Carbon steel | LCB Carbon Steel | 316 Stainless Steel |
Valve Plug | 416 Stainless
Steel | 420 Stainless Steel | 316 Stainless Steel |
Cage | 17-4PH Stainless steel | 17-4PH Stainless steel | 316 Stainless Steel with Electroless Nickel |
Disk Seat | 316 Stainless
Steel | – | 316 Stainless Steel |
Seat Ring | 410 or 416 Stainless Steel | 17-4PH Stainless steel | 316 Stainless Steel |